Description
The U.S. Sector strategy allocates dynamically between four long U.S. sector sub-strategies. Each of the four long sub-strategies use different momentum and mean reversion criteria
Due to the low correlation of these strategies, the combination creates a strategy with a considerably higher Sharpe Ratio than a simple sector rotation.
The strategy uses SPDR sector ETFs, but you can replace these with the corresponding sector ETFs or futures from other issuers.
US sectors have historically been good for trend following systems because each sector usually over or under performs for long periods at a time due to longer lasting economic cycles and not just short-term market fluctuations.
The economy itself is not a linear stable system, but swings between periods of expansion (growth) and contraction (recession). This results in a series of market cycles which are visualized in the following picture.
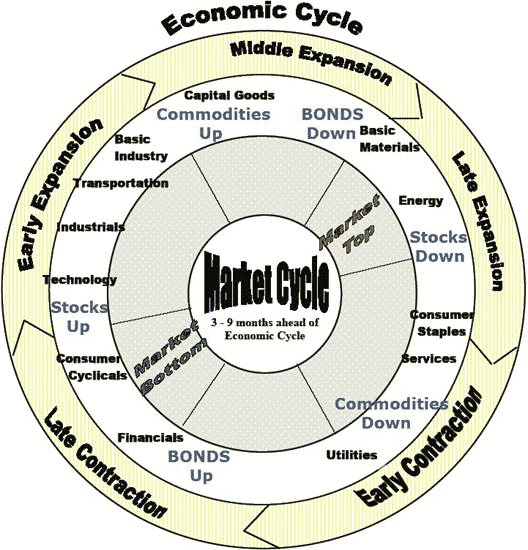
Source: http://www.nowandfutures.com (Global Business Cycles)
Each market cycle favors different industry sectors. The goal of a good working strategy is to choose the best performing sectors while avoiding or even shorting the worst performing sectors.
You can read the original strategy whitepaper for more details.
Methodology & Assets
U.S. industry sectors ETFs, their corresponding inverse or short sector ETFs and optional futures:
| U.S. Sector | ETF | Inverse (leverage) | Globex Futures |
| Materials | XLB | SMN (-2x) | IXB |
| Energy | XLE | ERY (-3x) | IXEe |
| Financial | XLF | SKF (-2x) | IXM |
| Industrials | XLI | SIJ (-2x) | IXI |
| Technology | XLK | REW (-2x) | IXT |
| Consumer Staples | XLP | SZK (-2x) | IXR |
| Real Estate | XLRE | SRS (-2x) | - |
| Utilities | XLU | SDP (-2x) | IXU |
| Health Care | XLV | RXD (-2x) | IXV |
| Consumer Discretionary | XLY | SCC (-2x) | IXY |
Statistics (YTD)
TotalReturn:
'Total return, when measuring performance, is the actual rate of return of an investment or a pool of investments over a given evaluation period. Total return includes interest, capital gains, dividends and distributions realized over a given period of time. Total return accounts for two categories of return: income including interest paid by fixed-income investments, distributions or dividends and capital appreciation, representing the change in the market price of an asset.'
Which means for our asset as example:- Compared with the benchmark SPY (94.2%) in the period of the last 5 years, the total return, or increase in value of 57.5% of US Sector Rotation Strategy is lower, thus worse.
- During the last 3 years, the total return, or increase in value is 25.9%, which is lower, thus worse than the value of 81.9% from the benchmark.
CAGR:
'Compound annual growth rate (CAGR) is a business and investing specific term for the geometric progression ratio that provides a constant rate of return over the time period. CAGR is not an accounting term, but it is often used to describe some element of the business, for example revenue, units delivered, registered users, etc. CAGR dampens the effect of volatility of periodic returns that can render arithmetic means irrelevant. It is particularly useful to compare growth rates from various data sets of common domain such as revenue growth of companies in the same industry.'
Applying this definition to our asset in some examples:- Compared with the benchmark SPY (14.3%) in the period of the last 5 years, the compounded annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.6% of US Sector Rotation Strategy is lower, thus worse.
- Compared with SPY (22.2%) in the period of the last 3 years, the annual return (CAGR) of 8% is lower, thus worse.
Volatility:
'Volatility is a statistical measure of the dispersion of returns for a given security or market index. Volatility can either be measured by using the standard deviation or variance between returns from that same security or market index. Commonly, the higher the volatility, the riskier the security. In the securities markets, volatility is often associated with big swings in either direction. For example, when the stock market rises and falls more than one percent over a sustained period of time, it is called a 'volatile' market.'
Which means for our asset as example:- The volatility over 5 years of US Sector Rotation Strategy is 11.7%, which is smaller, thus better compared to the benchmark SPY (17%) in the same period.
- Looking at volatility in of 8.9% in the period of the last 3 years, we see it is relatively lower, thus better in comparison to SPY (15.1%).
DownVol:
'Downside risk is the financial risk associated with losses. That is, it is the risk of the actual return being below the expected return, or the uncertainty about the magnitude of that difference. Risk measures typically quantify the downside risk, whereas the standard deviation (an example of a deviation risk measure) measures both the upside and downside risk. Specifically, downside risk in our definition is the semi-deviation, that is the standard deviation of all negative returns.'
Which means for our asset as example:- Looking at the downside volatility of 8.4% in the last 5 years of US Sector Rotation Strategy, we see it is relatively lower, thus better in comparison to the benchmark SPY (11.7%)
- Looking at downside volatility in of 6.3% in the period of the last 3 years, we see it is relatively lower, thus better in comparison to SPY (10.1%).
Sharpe:
'The Sharpe ratio was developed by Nobel laureate William F. Sharpe, and is used to help investors understand the return of an investment compared to its risk. The ratio is the average return earned in excess of the risk-free rate per unit of volatility or total risk. Subtracting the risk-free rate from the mean return allows an investor to better isolate the profits associated with risk-taking activities. One intuition of this calculation is that a portfolio engaging in 'zero risk' investments, such as the purchase of U.S. Treasury bills (for which the expected return is the risk-free rate), has a Sharpe ratio of exactly zero. Generally, the greater the value of the Sharpe ratio, the more attractive the risk-adjusted return.'
Applying this definition to our asset in some examples:- Looking at the ratio of return and volatility (Sharpe) of 0.61 in the last 5 years of US Sector Rotation Strategy, we see it is relatively lower, thus worse in comparison to the benchmark SPY (0.69)
- During the last 3 years, the risk / return profile (Sharpe) is 0.62, which is smaller, thus worse than the value of 1.3 from the benchmark.
Sortino:
'The Sortino ratio, a variation of the Sharpe ratio only factors in the downside, or negative volatility, rather than the total volatility used in calculating the Sharpe ratio. The theory behind the Sortino variation is that upside volatility is a plus for the investment, and it, therefore, should not be included in the risk calculation. Therefore, the Sortino ratio takes upside volatility out of the equation and uses only the downside standard deviation in its calculation instead of the total standard deviation that is used in calculating the Sharpe ratio.'
Using this definition on our asset we see for example:- Looking at the ratio of annual return and downside deviation of 0.84 in the last 5 years of US Sector Rotation Strategy, we see it is relatively lower, thus worse in comparison to the benchmark SPY (1)
- Compared with SPY (1.95) in the period of the last 3 years, the downside risk / excess return profile of 0.87 is lower, thus worse.
Ulcer:
'The ulcer index is a stock market risk measure or technical analysis indicator devised by Peter Martin in 1987, and published by him and Byron McCann in their 1989 book The Investors Guide to Fidelity Funds. It's designed as a measure of volatility, but only volatility in the downward direction, i.e. the amount of drawdown or retracement occurring over a period. Other volatility measures like standard deviation treat up and down movement equally, but a trader doesn't mind upward movement, it's the downside that causes stress and stomach ulcers that the index's name suggests.'
Applying this definition to our asset in some examples:- Compared with the benchmark SPY (8.42 ) in the period of the last 5 years, the Ulcer Ratio of 6.51 of US Sector Rotation Strategy is lower, thus better.
- During the last 3 years, the Downside risk index is 4.12 , which is higher, thus worse than the value of 3.4 from the benchmark.
MaxDD:
'Maximum drawdown measures the loss in any losing period during a fund’s investment record. It is defined as the percent retrenchment from a fund’s peak value to the fund’s valley value. The drawdown is in effect from the time the fund’s retrenchment begins until a new fund high is reached. The maximum drawdown encompasses both the period from the fund’s peak to the fund’s valley (length), and the time from the fund’s valley to a new fund high (recovery). It measures the largest percentage drawdown that has occurred in any fund’s data record.'
Applying this definition to our asset in some examples:- Compared with the benchmark SPY (-24.5 days) in the period of the last 5 years, the maximum reduction from previous high of -16.4 days of US Sector Rotation Strategy is larger, thus better.
- During the last 3 years, the maximum reduction from previous high is -11.7 days, which is higher, thus better than the value of -18.8 days from the benchmark.
MaxDuration:
'The Drawdown Duration is the length of any peak to peak period, or the time between new equity highs. The Max Drawdown Duration is the worst (the maximum/longest) amount of time an investment has seen between peaks (equity highs) in days.'
Which means for our asset as example:- Compared with the benchmark SPY (488 days) in the period of the last 5 years, the maximum time in days below previous high water mark of 507 days of US Sector Rotation Strategy is larger, thus worse.
- Compared with SPY (87 days) in the period of the last 3 years, the maximum time in days below previous high water mark of 270 days is greater, thus worse.
AveDuration:
'The Drawdown Duration is the length of any peak to peak period, or the time between new equity highs. The Avg Drawdown Duration is the average amount of time an investment has seen between peaks (equity highs), or in other terms the average of time under water of all drawdowns. So in contrast to the Maximum duration it does not measure only one drawdown event but calculates the average of all.'
Applying this definition to our asset in some examples:- Looking at the average days under water of 150 days in the last 5 years of US Sector Rotation Strategy, we see it is relatively greater, thus worse in comparison to the benchmark SPY (119 days)
- During the last 3 years, the average days under water is 71 days, which is greater, thus worse than the value of 19 days from the benchmark.
Performance (YTD)
Allocations and holdings shown below are delayed by one month.
Register now to get the current trading allocations.
Allocations ()
Returns (%)
- Note that yearly returns do not equal the sum of monthly returns due to compounding.
- Performance results of US Sector Rotation Strategy are hypothetical and do not account for slippage, fees or taxes.
- Results may be based on backtesting, which has many inherent limitations, some of which are described in our Terms of Use.
